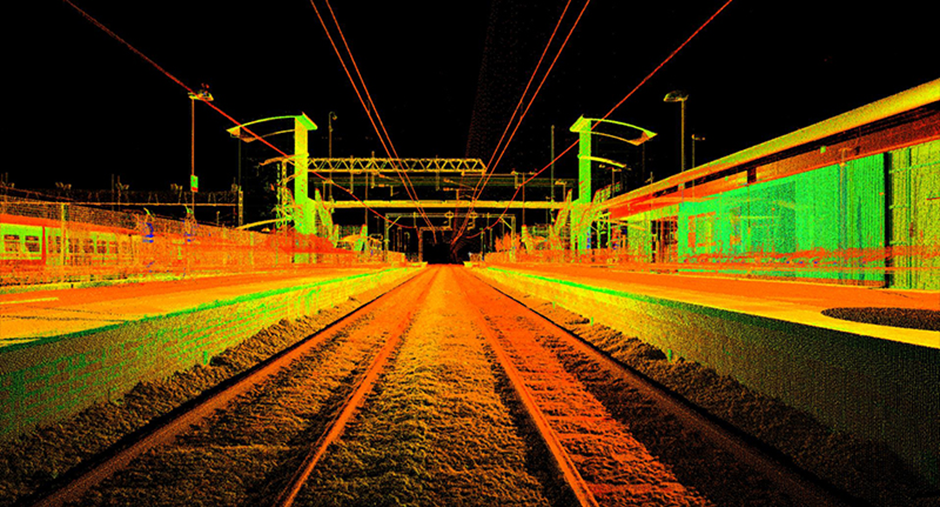
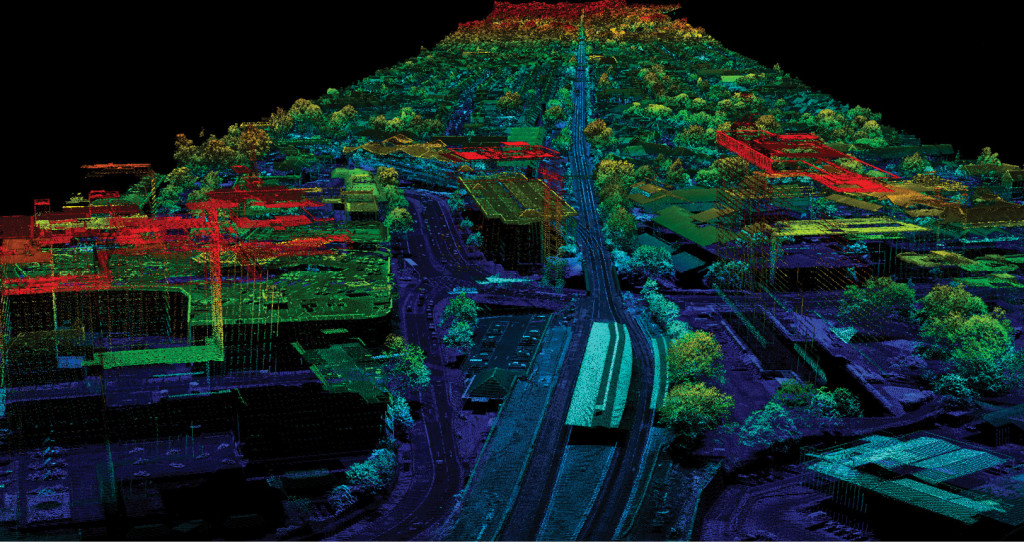
Laser Scanning
Laser scanning utilizes laser scanners to collect data by controlling laser beam deflection. These scanners can remotely capture the surface shape and several internal layers of buildings, objects, and landscapes. The shape of structures, items or landscapes is referred to as a point cloud by defined by millions of points.
Once the data is collected, the complicated information sets are provided to generate deliverables by means of software in a 3D format. 3D laser scanning improves the entire design experience with reduced errors and reduces costs in comparison with conventional information collection methods.
3D laser scanning is used widely for scanning buildings and their interiors in the architecture, engineering and construction industry. The “As-Built” condition of the site is also utilized by process industry, public authorities, museums, forensics and new-age barcode readers, space flight and laser shows.
LIDAR SERVICES
LiDAR stands for Light Detection and Ranging. It is a remote sensing technology which uses laser beams to evaluate the distance between target objects. It is widely used to provide high-level terrain precision, particularly in forestry and locations where physical evaluation or data collection is not viable. Physical assessment of the region or photography may not be possible and may produce incorrect outcomes in challenging topographies like hills, dense vegetation, water bodies, etc. In such situations, laser scanners / sensors are used to accurately capture data.
LiDAR can be used in agricultural, archeological, military, geological, autonomous driving, mining, transport, renewable energy, astronomy and forest management industries. LiDAR can allow geologists and hydrologists to explore and evaluate water bodies, rocks, tree cover, etc. using laser beams. We have been involved in projects where a government wanted to build a dam. LiDAR technology was used to evaluate the land, define the appropriate solution for the water catchment region and provide precise outcomes required to construct the dam.
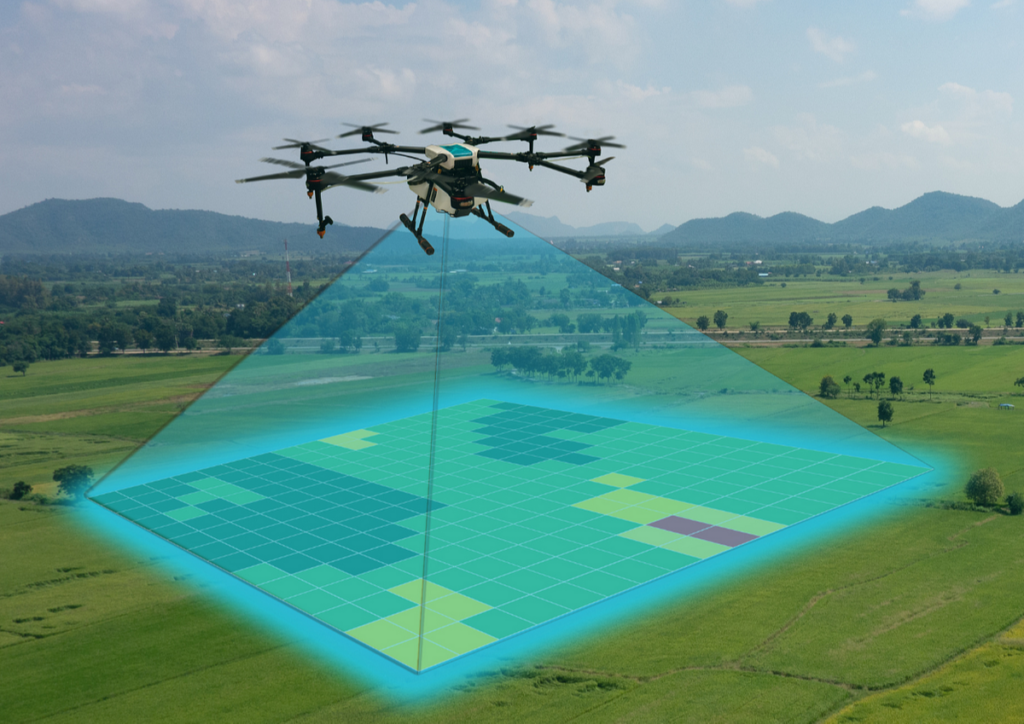

Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry is used to extract meaningful object and environment data via aerial, satellite, and UAV imagery. It’s essentially the science of photographic measurements to obtain real-world data. The pictures recorded are further categorized, evaluated and analyzed using photogrammetry methods, and lastly displayed in 3D format.
For example, in the event of a natural disaster, say flood, pictures are taken by satellite or drone; photogrammetry can assist insurance companies by accurately measuring the regions that are susceptible to flooding, including impacted structures, agricultural regions, utility services and field modifications. This allows for a precise assessment of the impacted region, provides a 3D view of the region, without the need to leave the office. Therefore, rejecting any false insurance claims.
Data Conversion
Simply put, data conversion is nothing but converting information from one format to another. An incorrect data format can be a major source of operational hindrance while data moves through several applications. For every organization, converting information to the specified format is therefore critical today.
The encrypted geographical format is transformed to a specific file in GIS data conversion. In the process of information development, several steps are engaged. It starts with extracting data and continues to data entry, data integration, data migration, data maintenance, database design, data loading and concludes in a data conversion phase.
The conversion of GIS data is commonly used in different sectors such as utilities, AEC, oil & gas, real estate and so on.
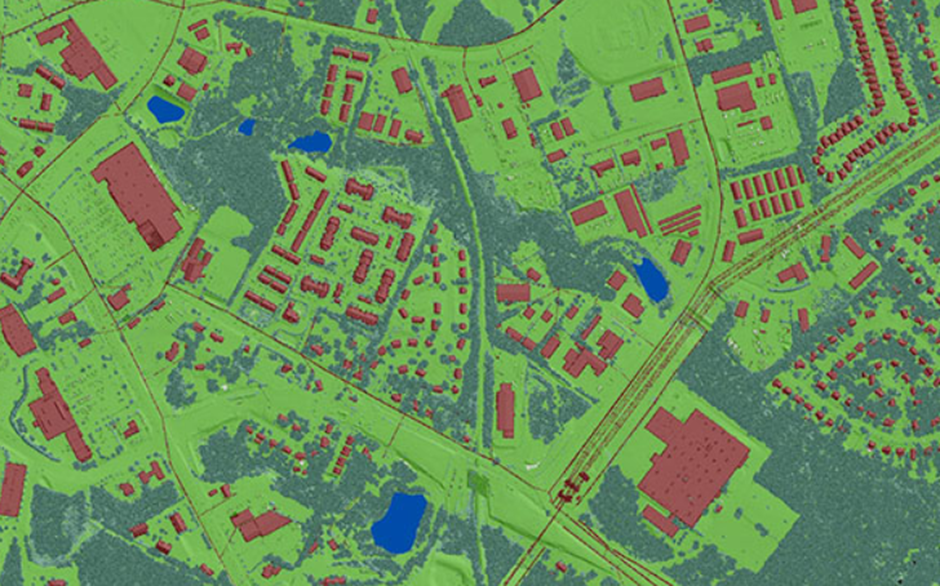

Building Information Modeling
BIM is an acronym for Building Information Modelling. It is a technique to generate and manage digital representations of a building with both functional and physical features. By facility, we mean building areas, such as infrastructure, buildings, transportation, etc.
BIM is used throughout the life cycle of a construction facility. Traditional designs of buildings were based on 2D technical drawings. The scope of BIM extends beyond 3D and currently, can go up to 7D.
In a 3D format, BIM merely enhances the fundamental spatial dimensions of a construction, i.e. width, height and depth. These dimensions expand basis the requirements. For example, time is the fourth dimension, costs are the fifth dimension; environmental assessment and sustainability analysis is used for 6D and management of lifecycles is a component of 7D BIM models. BIM is used across different industries, such as architecture, engineering, construction, utilities, transportation, and the likes.
BIM can, for example virtually represent the construction of an establishment in the building industry before it is built. This would facilitate to better planning, save time, reduce risks, minimize onsite waste, improve safety, provide a fully coordinated model, facilitates documentation for future renovation while analysing and simulating potential impact.
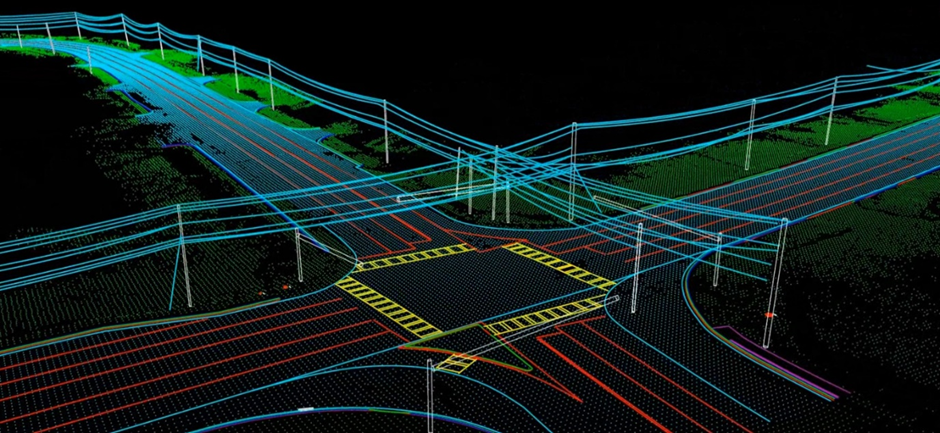


We are a preferred provider of 3D topographic mapping, surface modelling, 3D asset extraction, sub-station modeling, and related mobile mapping services. Mobile mapping services from DM Technologies Pvt. Ltd aid customers to receive precise 3D navigation information by virtually displaying 3D maps of your property and producing 3D surface models.
The data facilitates new alignment planning, asset management, and generates accurate HD maps. Our services are applied in, but not limited to, online mapping systems, emergency response planning, road mapping, and road facilities management. Our comprehensive map layouts are specifically tailored to customer requirements so that customers can use them as reference material for designing and re-designing road networks, bridges, waterways, among many others
Mobile Mapping
Mobile mapping is essential for capturing urban data and is often used in 3D urban modelling. Transportation authorities have used them extensively to map their assets.
A variety of remote sensing technologies such as Photographs, LiDAR, Radar, etc., collect geospatial information. The information gathered by means of a remote sensor installed on a mobile platform is called mobile mapping (SUV, train, boat etc.).
The mobile platform is generally driven through a planned path to obtain data relating to the Spatial Model, such as 3D point cloud and appropriate pictures. The data cannot be gathered by static sensors accurately. In general, the mobile platform is mounted with calibrated digital cameras, LiDAR sensors, GPS and inertial sensors to accurately capture information.
Our Core Values
Integrity
We believe open and honest relationships with our customers and our employees are the only way to do business
Collaboration
We are community of business professionals providing both global and local perspective, we share ideas and work together to meet our business objectives.
Quality
Engage right people with the right experience and delivery best in class services to our trusted clients
Innovation
We foster creativity and adaptability, to consistently explore new way of delivering value.
Recognition
We believe in recognizing the involvement of our people. We support, encourage, celebrate their contributions
Pross Flow

Case Studies
Process Layout: Skids
- Brief Scope: To create a 3dModel
- Input : 3d Point cloud data.
- Output : 3d CAD Model
- Duration : 900 Man-Hours
- Team Size: 8
- CHALLENGES: The main challenge is to model the Heavy dense Pipe lines and the flow-meters, valves, evacuators and clamps.
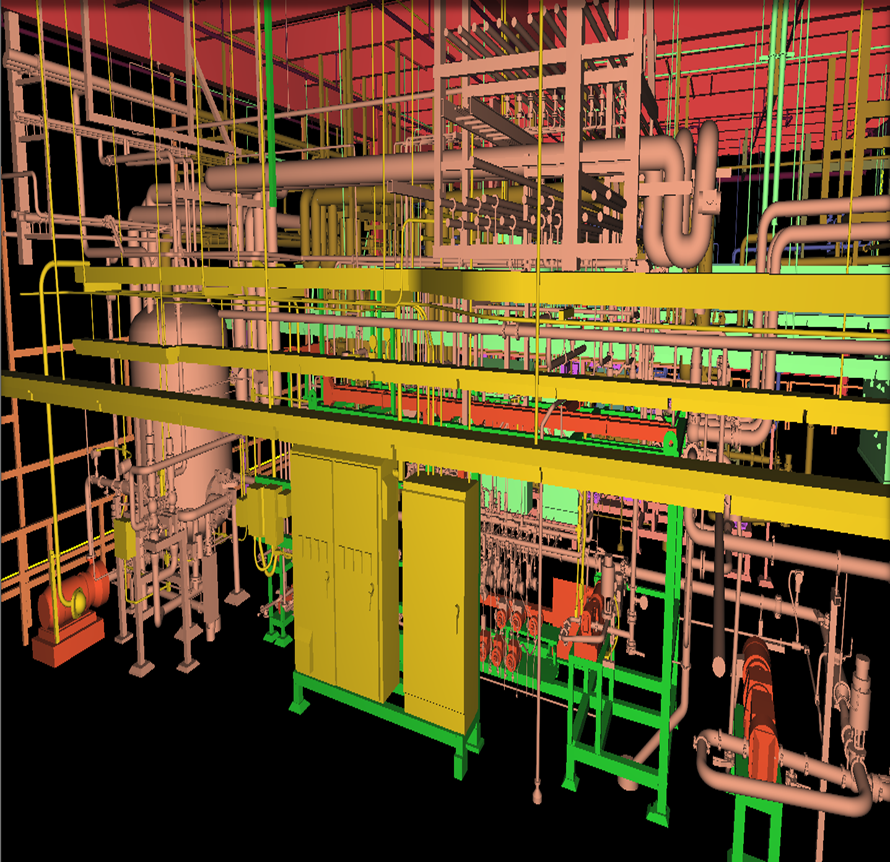

Industrial Layout : Process Plants
- Brief Scope: To create a 3dModel
- Input : 3d Point cloud data.
- Output : 3d CAD & INVENTOR Dump Model
- Duration : 450 Man-Hours
- Team Size: 5
- CHALLENGES: The main challenge is to model the intricate shapes of the equipment’s and inter link the equipment flow and Piping flow from Floor to Floor.
Shipbuilding
- Brief Scope: To create a 3d as built Model
- Input : 3d Point cloud data & Photos.
- Output : 3d CAD model & PDMS Dump Model
- Duration : 250 Man-Hours.
- Team Size: 5.
- CHALLENGES: The quite challenging in this model is the stiffeners and outer shapes of the Ballast tanks. Due to the 3D structure of the ship.
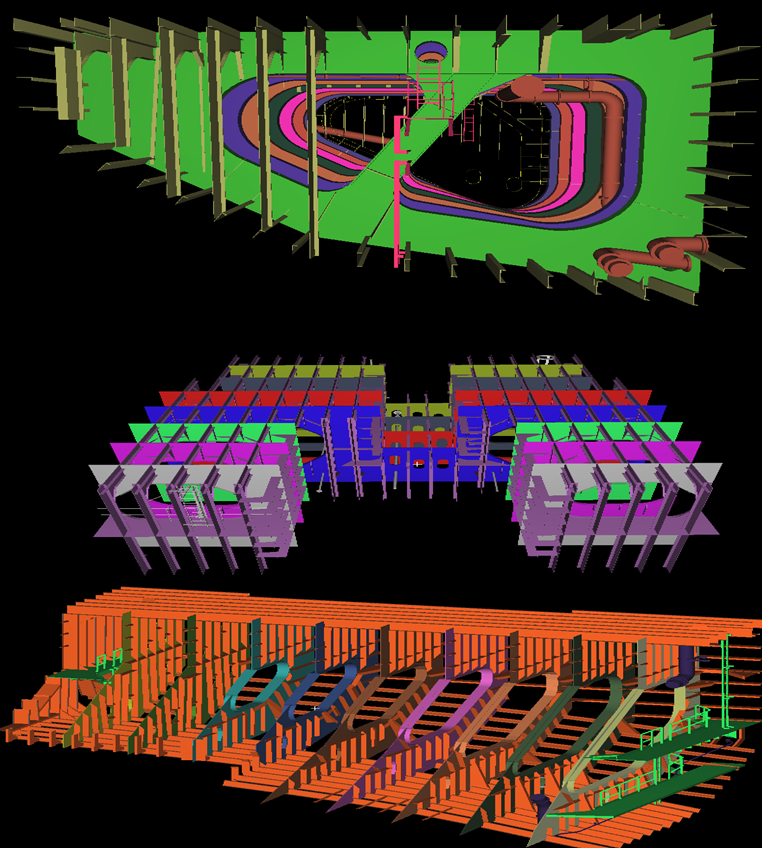

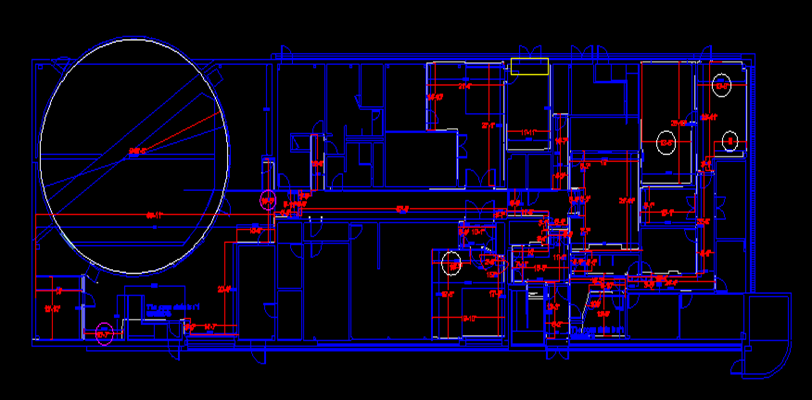
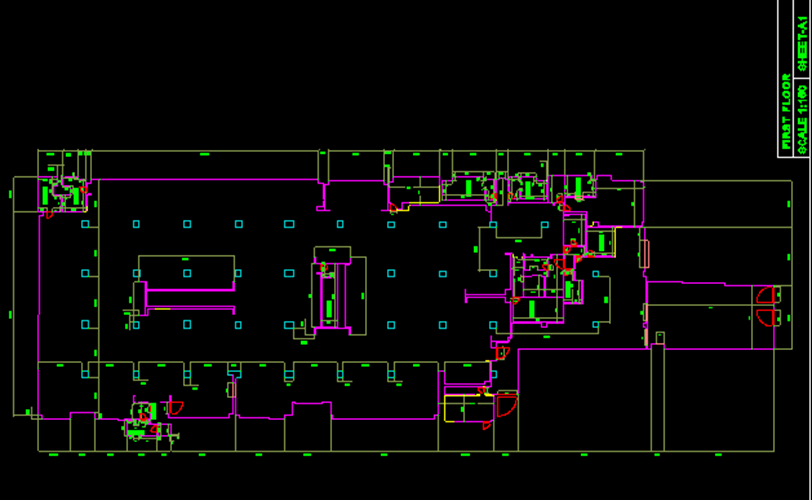
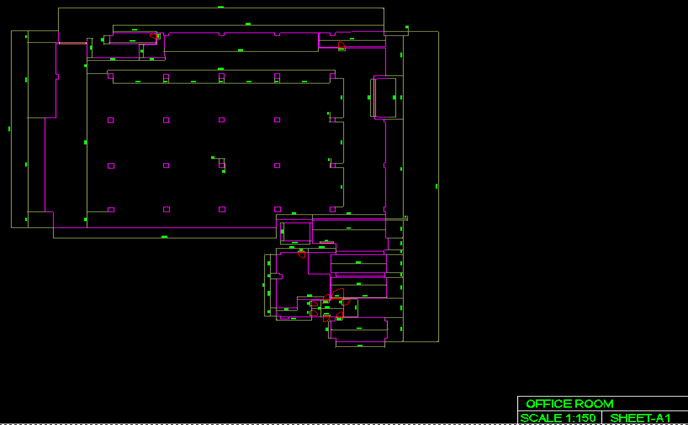
Architectural Modeling
- Brief Scope: To create a 3dModel & 2D Plans
- Input : 3d Point cloud data.
- Output : 3d CAD Model & 2D Plans
- Duration : 700 Man-Hours
- Team Size: 16
- CHALLENGES: The main challenge is to create the front elevation shape and the Doom shape of this building.
2D PLANS