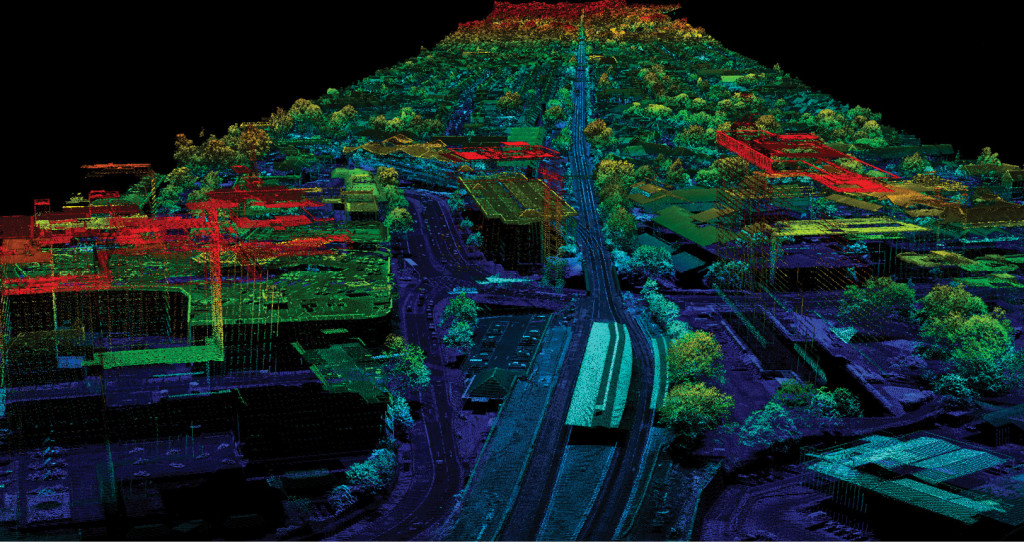
LIDAR SERVICES
LiDAR stands for Light Detection and Ranging. It is a remote sensing technology which uses laser beams to evaluate the distance between target objects. It is widely used to provide high-level terrain precision, particularly in forestry and locations where physical evaluation or data collection is not viable. Physical assessment of the region or photography may not be possible and may produce incorrect outcomes in challenging topographies like hills, dense vegetation, water bodies, etc. In such situations, laser scanners / sensors are used to accurately capture data.
LiDAR can be used in agricultural, archeological, military, geological, autonomous driving, mining, transport, renewable energy, astronomy and forest management industries. LiDAR can allow geologists and hydrologists to explore and evaluate water bodies, rocks, tree cover, etc. using laser beams. We have been involved in projects where a government wanted to build a dam. LiDAR technology was used to evaluate the land, define the appropriate solution for the water catchment region and provide precise outcomes required to construct the dam.